Complete Guide to Flameproof Cable Glands: What, Why & Where?
- shreeelectrical
Complete Guide to Flameproof Cable Glands: What, Why & Where?
In industries that deal with explosive gases, dust, or vapors—such as oil & gas, petrochemical, and mining—safety isn’t just a priority; it’s a necessity. That’s where flameproof cable glands come into the picture. They serve a vital role in ensuring electrical safety in hazardous zones.
In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know about flameproof cable glands—what they are, how they work, why they’re important, and how to choose the right one.
What is a Flameproof Cable Gland?
A flameproof cable gland (also known as an explosion-proof or Ex d cable gland) is a mechanical device used to secure and seal the end of an electrical cable entering an enclosure that is certified for use in hazardous areas (Zone 1 & Zone 2). Its main purpose is to prevent the passage of flames or hot gases through the cable entry during an internal explosion.
These glands are specially engineered to contain any internal ignition and prevent it from propagating outside the enclosure into the potentially explosive external atmosphere.
Why Are Flameproof Cable Glands Important?
Flameproof cable glands are critical safety components in electrical systems installed within hazardous or explosive environments. These seemingly small devices play a massive role in preventing catastrophic incidents by maintaining the integrity of explosion-proof enclosures and ensuring safe cable terminations.
Let’s break down their importance in detail:
Prevents Explosion Propagation
The most vital role of a flameproof (Ex d) cable gland is to contain any internal explosion that may occur inside an electrical or instrumentation enclosure. Electrical components like switches, relays, and terminals can generate sparks or heat. If an explosive gas or vapor enters the enclosure, it could ignite inside.
Without a flameproof gland:
- The explosion can escape through the cable entry point.
- Escaping flames or hot gases can ignite the external atmosphere.
- This leads to chain-reaction explosions across the site.
Flameproof glands are engineered to withstand and contain such internal explosions and ensure no flame transmission to the external hazardous zone.
Maintains Flameproof Integrity of the Enclosure
A flameproof-rated enclosure is only effective if all its openings are sealed to the same protection standard. Cable entries are the most vulnerable points in any explosion-proof system.
Flameproof glands:
- Provide flame-arresting paths through tightly machined threads and components.
- Work as part of the overall flameproof "Ex d" system, maintaining compliance with IEC/ATEX/UL safety requirements.
If the cable gland is not flameproof, the entire system's certification becomes invalid, risking both life and infrastructure.
Prevents Ingress of Flammable Gases, Dust, or Moisture
Hazardous areas often have extreme environmental conditions, such as:
- High humidity
- Corrosive vapors
- Flammable dust clouds
- Heavy rain or water exposure
Flameproof cable glands offer high ingress protection (IP66/IP68), ensuring:
- No entry of external gases or dusts into the enclosure.
- Long-term environmental protection, preventing internal corrosion or short circuits.
- Continuous performance even in outdoor, offshore, or underground applications.
Prevents Gas Migration Through Cable Cores
In some scenarios, flammable gases may travel through the internal layers of multi-core cables (a phenomenon called gas migration). This is especially risky because:
- It bypasses the physical flameproof barriers.
- Gases can reach non-rated enclosures and ignite.
To counter this, barrier-type flameproof glands are used. These include:
- A compound or resin barrier that fills gaps between cable cores.
- A complete gas-tight seal to prevent any internal leakage paths.
This is especially important in Zone 1 or Gas Group IIC areas, where even a small leak could be disastrous.
Provides Mechanical Strength and Strain Relief
Industrial environments subject cables to:
- Vibration
- Mechanical pulling
- Bending or twisting
- Thermal expansion
Flameproof cable glands:
- Clamp the cable firmly to prevent movement.
- Ensure the cable jacket remains undamaged.
- Maintain a tight seal even under stress.
This prevents accidental loosening, which could expose live wires or compromise the flameproof barrier.
Supports Safe Operations and Reliability
Flameproof cable glands contribute to:
- Safe, uninterrupted plant operations
- Longer equipment life
- Reduced maintenance needs
- Increased operator confidence
In high-risk industries, safety equals productivity. A single explosion incident can cause millions in damages and lost production time.
How Do Flameproof Cable Glands Work?
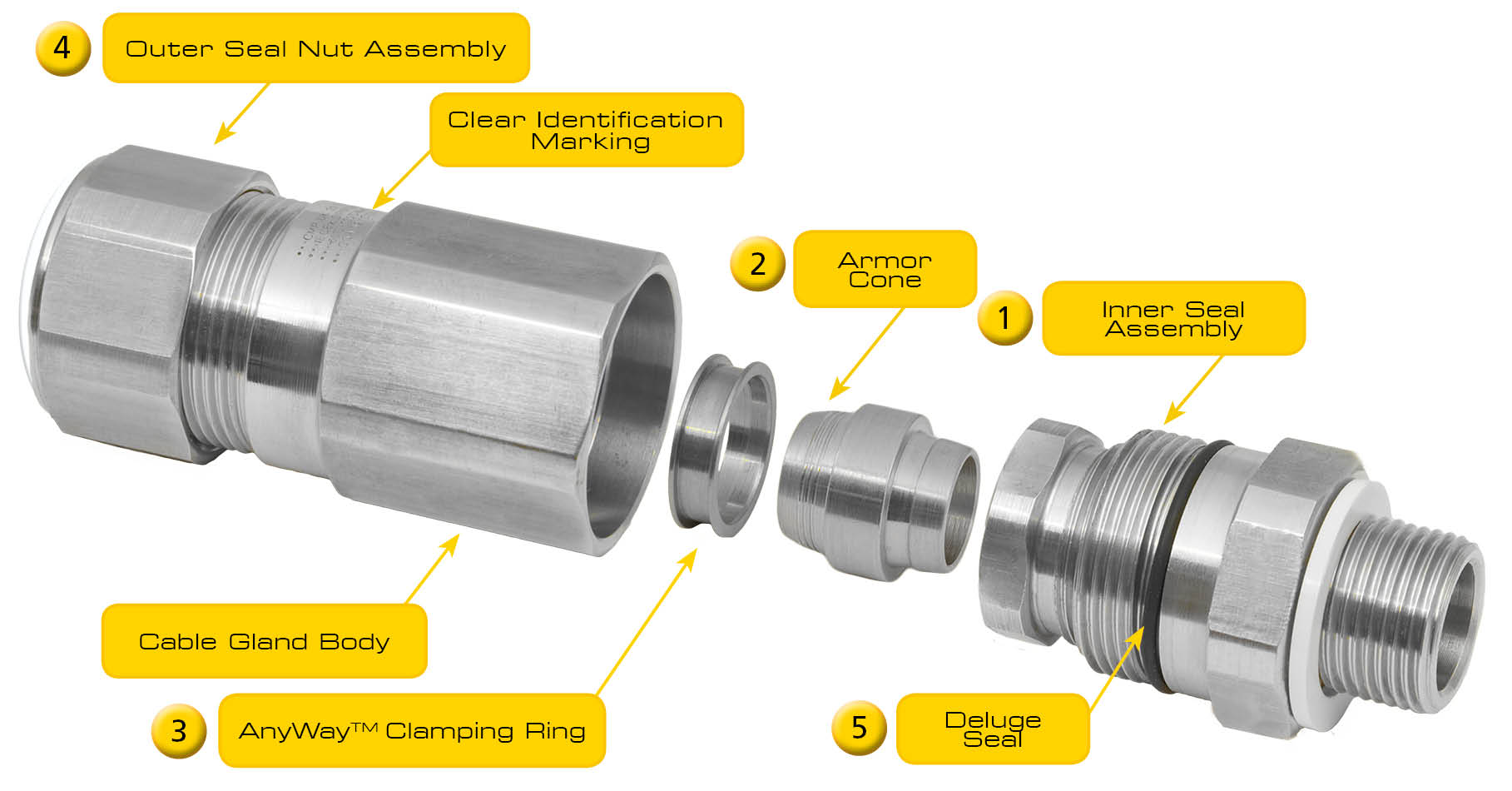
The gland creates a pressure-tight and flame-arresting seal around the cable. If an explosion occurs inside the enclosure:
- Containment: The cable gland, being part of the flameproof boundary, contains the pressure.
- Cooling of Flames: Any hot gases trying to escape through the gland’s threads are cooled and restricted by tight clearances and long flame paths.
- Mechanical Retention: The gland provides a strong grip and strain relief to prevent cable movement.
Types of Flameproof Cable Glands
There are several types depending on application and cable type:
1) ET Thread Glands 1/2 inches to 4 Inch/ 100mm OD.
2) NPT Thread Glands 1/2 inches to 4 Inch
3) Matrix Thread Glands 12mm to 100mm OD.
4) PG Glands 1/2 inch to 4 Inch/ 100mm OD.
Final Thoughts
Flameproof cable glands are not just mechanical fittings—they are safety-critical components engineered to work under extreme conditions. Whether you're installing a control panel in a chemical plant or wiring up a sensor on an oil rig, the right cable gland ensures:
- The safety of personnel
- The reliability of equipment
- Compliance with international explosion protection standards
Always choose certified products and ensure they are correctly installed and maintained to guarantee protection in hazardous environments.


